Tutorials
Example: Mutual exclusive Srsf1 and Srsf2 binding on exons
SR proteins are RNA-binding proteins that are associated with alternative splicing, and recent findings suggest that they are involved in both exon skipping and inclusion events (Pandit et al. 2013). Furthermore, Pandit et al. suggest although Srsf1 and Srsf2 binding sites largely target the same exons, certain exons are regulated by only one of the two factors, such that there is mutually exclusive binding of Srsf1 or Srsf2. Exactly these exons can be identified with doRiNA 2 in the following manner:
As we're not uploading a custom regulator, we just click the blue "Search" button on the left side of the start page.
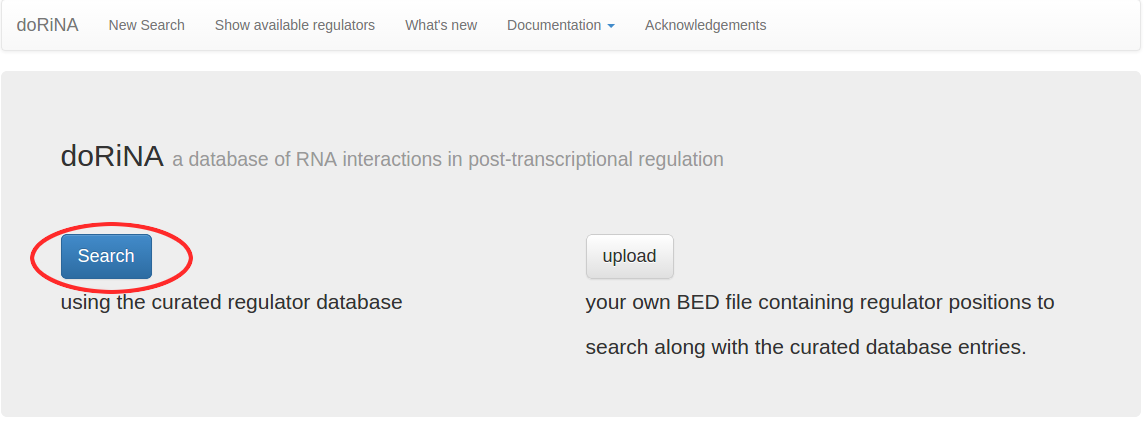
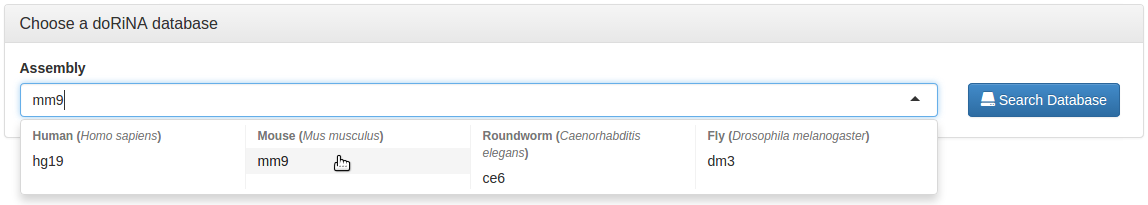
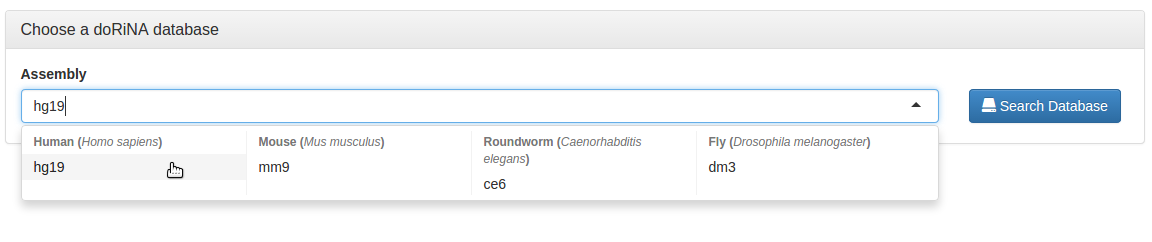
Having clicked "Search", we now can select the organism and assembly we want to work with. We select the mouse assembly "mm9", and click the "Search Database" button.
In the search page, we can build up the search we are interested in. We don't want to limit our search to a set of candidate genes, so we ignore that option. As we are only interested in exons, we select "CDS" in the "Look for binding sites in region" settings. Then we use the autocompletion option of the "Regulators (set A)" field to quickly find the Srsf1 HITS-CLIP dataset by typing "Srsf1" and hitting the return key. Alternatively, we could have used the mouse to select the entry, or even just scrolled the list without narrowing down the displayed regulators.
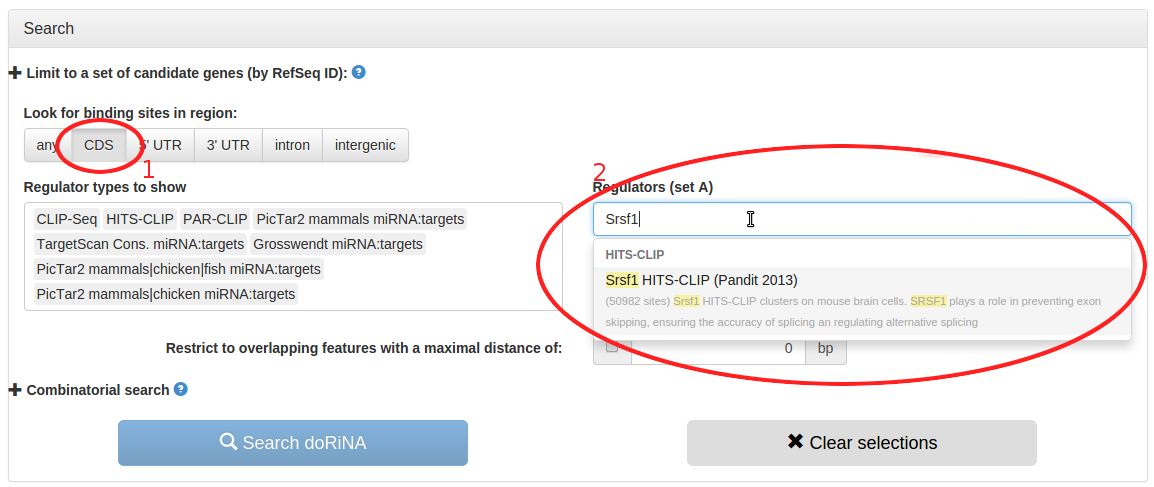
- Look for binding sites in CDS regions only
- Type "Srsf1" into the "Regulators (set A)" field to search for the Srsf1 HITS-CLIP dataset
Now to repeat the process for Srsf2, we first expand the combinatorial search settings by clicking on "Combinatorial search". Then we again look for binding sites in CDS regions and pick the Srsf2 HITS-CLIP dataset for "Regulators (set B)". As we are interested in mutually exclusive binding, we use the "XOR" (exclusive or) set operation. Then, we click the blue "Search doRiNA" button to start the search.
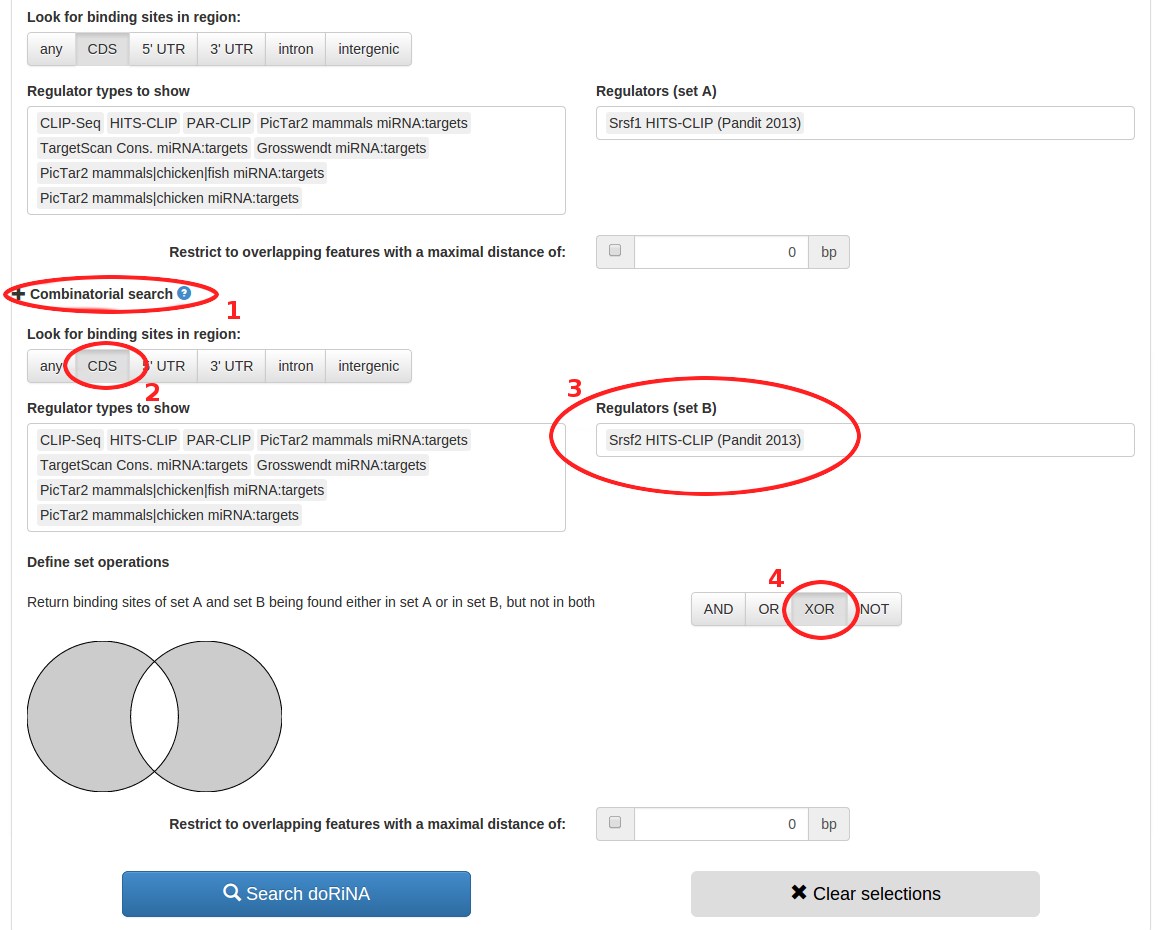
- Expand the combinatorial search pane
- Look for binding sites in CDS regions only
- Type "Srsf2" into the "Regulators (set B)" field to search for the Srsf1 HITS-CLIP dataset
- Select XOR to search for mutually exclusive binding
- Click the blue "Search doRiNA" button to start the search
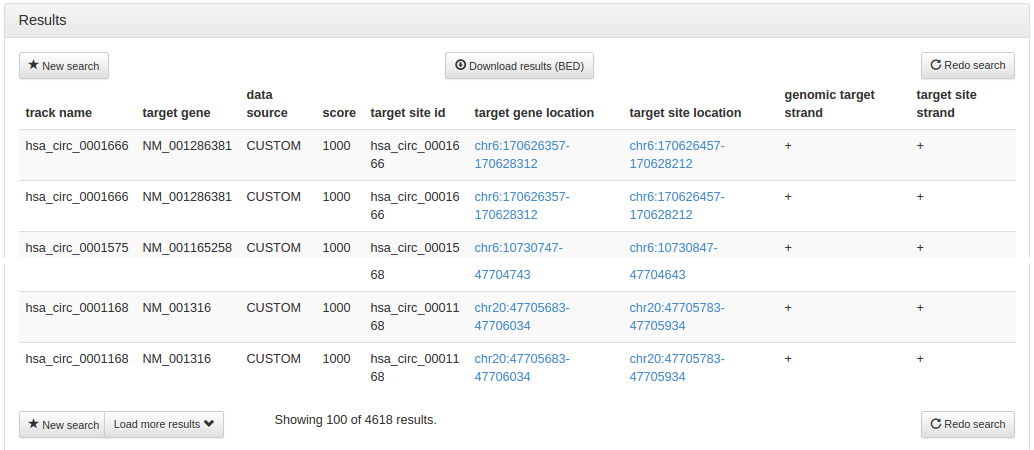
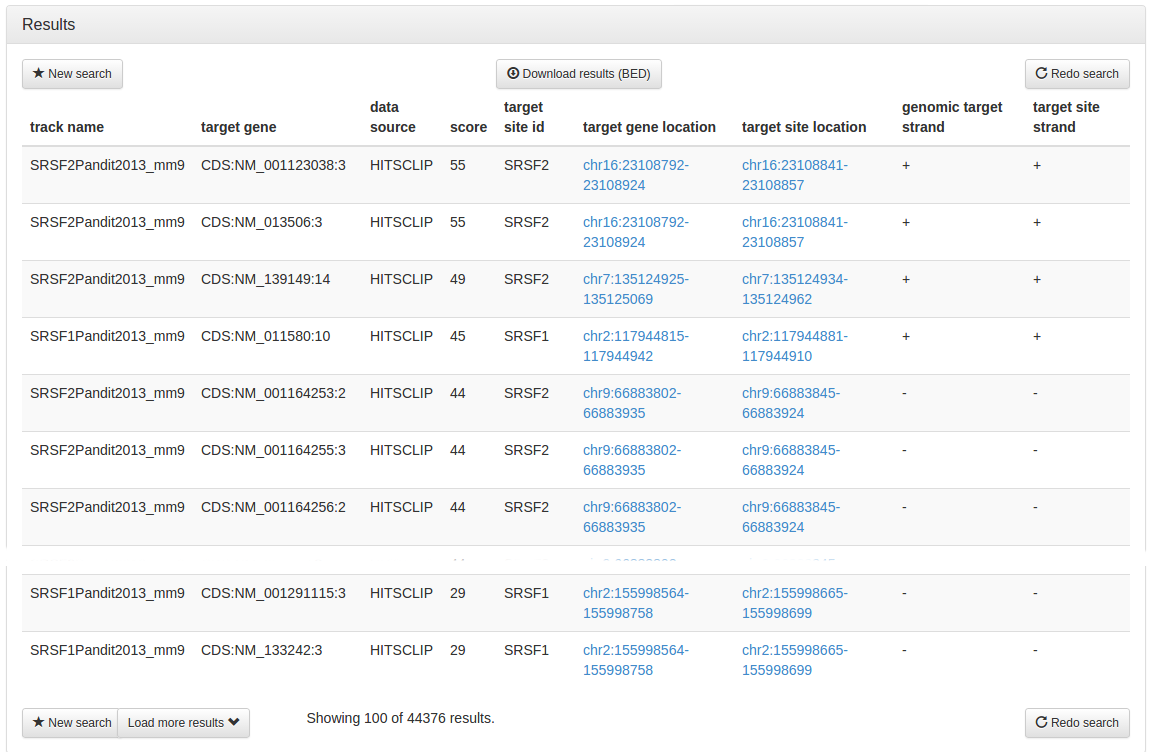
After a few seconds, the results page is displayed, giving 44,476 results that are bound by either Srsf1 or Srsf2, but not both. Buttons at the top and the bottom of the page allow you to start a new search (chose this if you want to search on a different assembly) or to go back to the search options to redo the search on the same assembly with changed search options. A button on the top of the page allows you to download the complete results in BED file format. To optimise loading times, the results page only displays the top 100 hits, a button on the bottom of the page allows you to load more results.
Example: Genic regions that form circular RNAs and overlap with Ago sites in HEK293 cells
Circular RNAs have emerged as a new regulatory RNA species in recent years (Wilusz & Sharp, 2013). The discovery that circRNAs act as "sponges" for miRNA highlights one of the potentially many regulatory roles of circRNAs. circRNAs are typically generated from primary transcripts that also give rise to linear transcript isoforms. Using a circRNA, we will show how to use the custom file upload. The BED file of all detected circles in HEK293 from the study of Memczak et al 2013 was downloaded from circBase.
We want to upload the HEK293 circRNA BED file from above, so we select "upload" this time around. This opens your browser's file dialog, browse and select the downloaded BED file.
The start page changes to reflect that a file was selected, now click "Go" to upload the file and start the search.
We can now select the organism and assembly we want to work with. We select the human assembly "hg19", and click the "Search Database" button.
On the search configuration page, the "uploaded custom regulator" is already pre-selected in
the "Regulators (set A) field. Using the interactive search, we type "ago2" to quickly find the
AGO2 CLIP-Seq regulator. Once we have selected that, we can decide if we want to require a match
to all of the multiple regulators for a hit or if a match to any regulator is sufficient. As we
are going to restrict our hits to circRNAs that are no more than 100 bp away from the RBP targets
in the "Restrict to overlapping features with a maximal distance" field, we can leave the "Regulators
that must match" on "any".
Expanding the "Combinatorial search" pane again, we select the "Regulators (set B)" field, and there
type "custom" to find our custom regulator. We then type "ago1234" to find the AGO1234 PAR-CLIP
regulator dataset. We can again leave "Regulators that must match" on "any", and we can also leave
"Define set operation" on "OR" to get the union of all results. Last but not least we again "Restrict
to overlapping features with a maximal distance" of 100 bp. Once that is done, we can click "Search
doRiNA" to start the search.
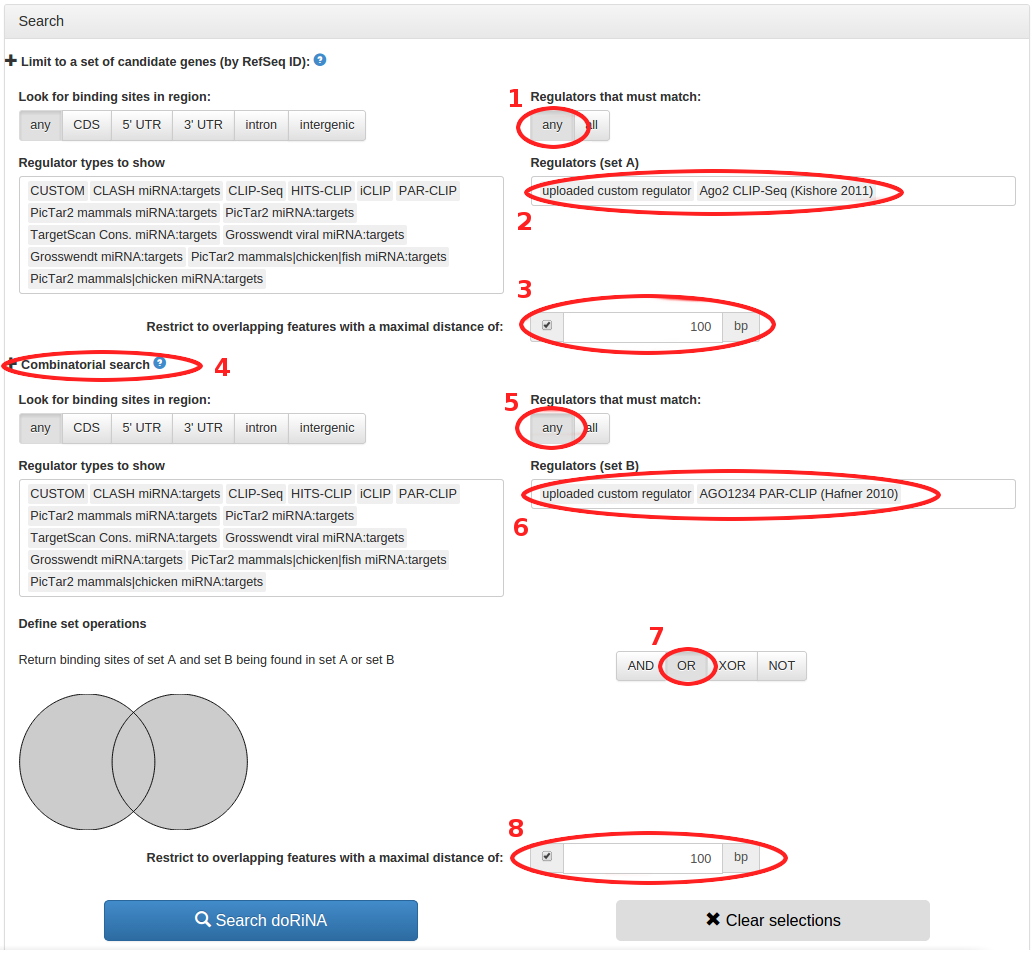
- Keep "Regulators that must match" on "any"
- "uploaded custom regulator" is already selected, type "ago2" in the "Regulators (set A)" field to quickly select the AGO2 CLIP-Seq dataset
- Limit search to circRNAs less than 100 bp away from AGO2 target sites
- Expand the combinatorial search
- Keep "Regulators that must match" on "any"
- In "Regulators (set B), first type "custom" to find the uploaded custom regulator, then type "ago1234" to find the AGO1234 PAR-CLIP dataset
- Keep "Define set operations" on OR to find the union of all the results
- Limit search to circRNAs less than 100 bp away from AGO1234 target sites
- Hit the "Search doRiNA" button to start the search
After a few seconds, the results page is displayed, giving 4,618 results. As we
requested the union of all results, we get a couple of hits where either circRNAs
overlap with other circRNAs or AGO sites overlap with each other. We can use the
download button at the top of the page to download the full results in BED file format,
and can then find after further analysis that 889 circRNAs are less than 100 bp away from
566 PAR-CLIP and 606 CLIP-Seq AGO target sites.
Buttons at the top of the page allow you to start a new search discarding your uploaded
regulator BED file or to redo the search, keeping your uploaded file around until that search
is completed. To optimise loading times, the results page only
displays the top 100 hits, a button on the bottom of the page allows you to load more
results.